Health
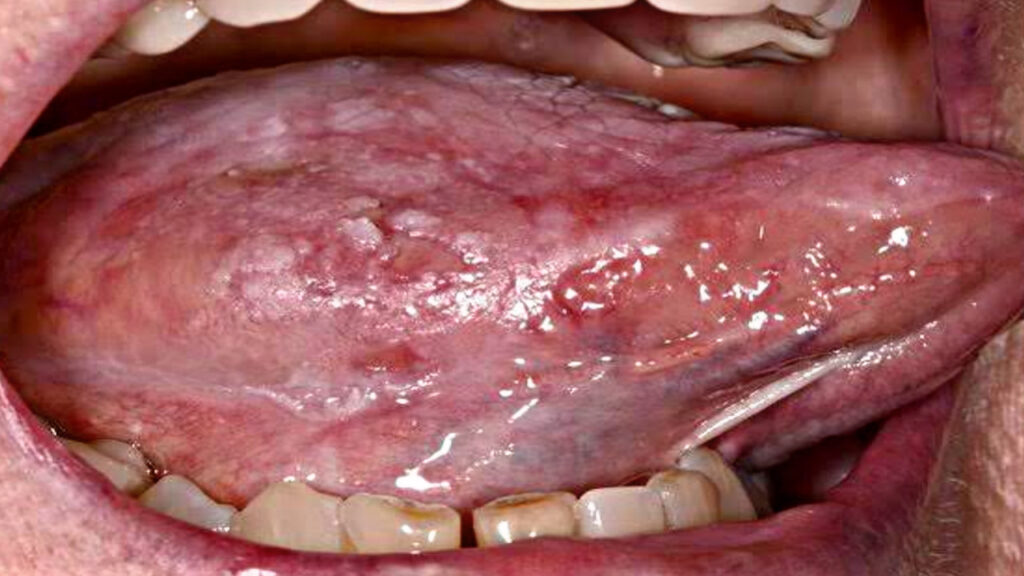
Mouth cancer, also known as oral cancer, refers to the abnormal growth of cells in the mouth, lips, tongue, gums, or inside the cheeks. It can be life-threatening if not detected early. In recent years, the number of cases has increased, making awareness and prevention crucial.
Causes of Mouth Cancer
There are several factors that may lead to the development of mouth cancer. Some of the most common causes include:
- Tobacco Use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or using chewing tobacco is one of the leading causes. Tobacco contains harmful chemicals that damage the lining of the mouth and can lead to cancer over time.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive drinking, especially when combined with tobacco use, increases the risk significantly. Alcohol can irritate the mouth and allow harmful substances to enter the cells.
- HPV Infection: The Human Papillomavirus (HPV), especially type 16, is known to be linked to throat and mouth cancers. It can be transmitted through oral sex.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Neglecting dental care can lead to infections and long-term inflammation, which may contribute to the development of cancerous cells in the mouth.
- Prolonged Sun Exposure: Exposure to the sun without protection can cause cancer on the lips, especially the lower lip.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immunity, whether due to medications or illness, are more vulnerable to mouth infections and cancers.
- Diet and Nutrition: A diet low in fruits and vegetables, which are rich in antioxidants, can increase the risk of developing cancer. Healthy foods help repair damaged cells and support the immune system.
Precautions to Prevent Mouth Cancer
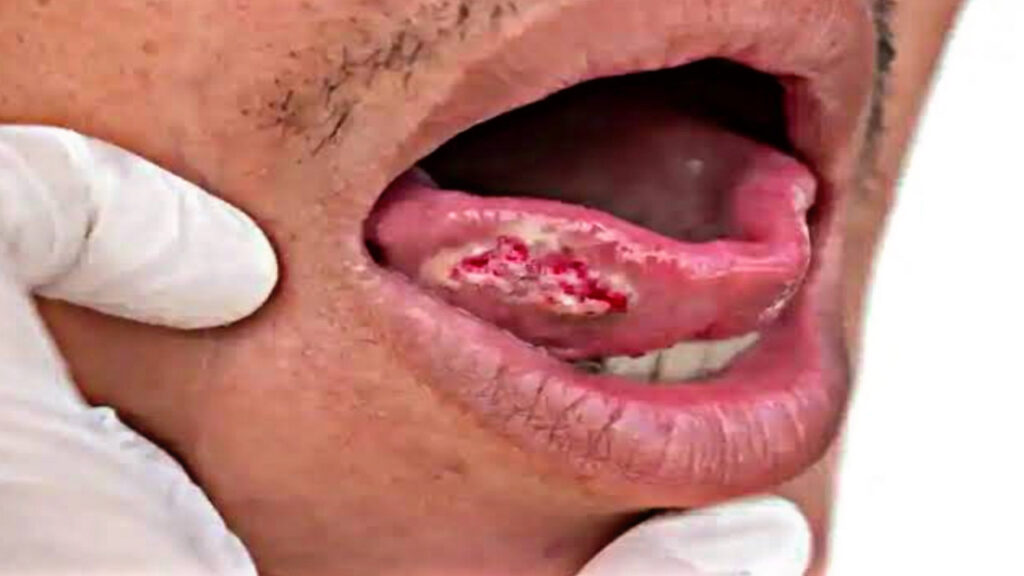
Taking certain precautions can greatly reduce your risk of developing mouth cancer. These include:
- Avoid Tobacco: Quitting smoking and chewing tobacco is the most effective way to lower your risk.
- Limit Alcohol: Drinking in moderation or not at all is highly recommended.
- Practice Safe Oral Sex: Use protection and be informed about your partner’s health to prevent HPV transmission.
- Protect Your Lips: Use a lip balm with SPF when going outdoors to reduce UV exposure.
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush and floss regularly, and visit a dentist at least twice a year for check-ups.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: Include fresh fruits and vegetables in your meals. They are rich in vitamins and help protect cells from damage.
- Regular Screenings: Early detection is key. If you notice sores, lumps, or persistent pain in the mouth, consult a doctor or dentist promptly.